Monday, 11 April 2011
Monday, 7 March 2011
Sunday, 6 March 2011
Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
High-grade PIN - Flat Pattern
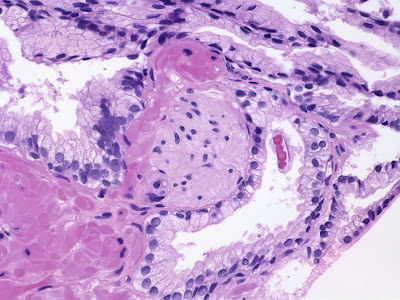
High-grade PIN – Tufted Variant
Six variants of high-grade PIN have been described – tufted, micropapillary, flat, cribriform, small cell type, and the most recent addition – inverted type. The image depicts tufted variant. Note the enlarged nuclei, prominent nucleoli and residual basal cells.
| The acinar epithelial cells are pseudostratified and arranged linearly in this example of flat variant of high-grade PIN. There is nuclear and nucleolar enlargement. Note the prominent apical snouts. |
High-grade PIN - Cribriform Pattern
In cribriform high-grade PIN interconnecting bridges of acinar epithelial cells extend across the lumen of the glands
High-grade PIN - Cribriform Pattern
Distinction of cribriform variant of high-grade PIN from adenocarcinoma may at times be extremely difficult. Immunostain for high molecular weight cytokeratin 34bE12 may be useful in such cases – basal cell layer is fragmented in PIN and absent in adenocarcinoma.
High-grade PIN - Tufted Pattern
Another example of tufted variant of high-grade PIN.
High-grade PIN & Cancer - 34bE12 Immunostain
The benign glands on upper right have continuous basal cell layer; high-grade PIN glands in the middle have fragmented basal cell layer; malignant glands on the left completely lack basal cell layer.
High-grade PIN - Prominent Nucleoli
This example of high-grade PIN shows all the classic histologic features: intermediate-to-large size preexisting glands displaying nuclear and nucleolar enlargement and fragmented basal cell layer.
High-grade PIN - Prominent Nucleoli
Another classic example of high-grade PIN, showing tufted and flat patterns.
High-grade PIN
High-grade PIN consists of intermediate to large size preexisting glands with proliferative changes resulting in hyperchromatic appearance. Note the small foci of cancer adjacent to PIN on the upper left and lower right.
High-grade PIN – Micropapillary Variant
he acinar epithelial cells are arranged in long, delicate, finger-like structures in this micropapillary variant. Atrophic acini are present at the bottom of the image.
Six variants of high-grade PIN have been described – tufted, micropapillary, flat, cribriform, small cell type, and the most recent addition – inverted type. The image depicts tufted variant. Note the enlarged nuclei, prominent nucleoli and residual basal cells.
Cardiac Pathology
please click here for cardiac pathology
http://www.slideworld.org/slideshow.aspx/Cardiac-Pathology-ppt-5167
http://www.slideworld.org/slideshow.aspx/Cardiac-Pathology-ppt-5167
Prostate Hyperplasia (slides)
Prostate - Nodular Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of the median lobe of the prostate produces a polypoid mass that protrudes in the bladder lumen.
Basal Cell Hyperplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Basal cell hyperplasia is usually seen in the transition zone. Occasionally, it may be encountered in needle biopsies (which sample peripheral zone).
Basal Cell Hyperplasia - Higher Magnification
The nuclei are ovoid or round with finely reticular chromatin and rare punctate nucleoli. The cytoplasm is pale eosinophilic or clear
Clear Cell Cribriform Hyperplasia
Lobular clusters of glands with cribriform architecture
Clear Cell Cribriform Hyperplasia
The glandular clusters have punched out lumens. The cytoplasm is clear or pale eosinophilic. The nuclei are uniform and lack nucleoli. Basal cells can be clearly seen.
Stromal Hyperplasia with Atypia
Large atypical cells with hyperchromatic nuclei containing intranuclear vacuoles are interspersed between benign glands. Prostatic stromal hyperplasia with atypia
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
AAH encountered in a transurethral resection specimen.
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia - 34bE12 Immunostain
The immunostain for high molecular weight cytokeratin 34bE12 demonstrates fragmented basal cell layer in the previous focus of AAH.
Post-atrophic Hyperplasia
Clusters of atrophic prostatic acini with proliferative changes. At low magnification, it may be mistaken for adenocarcinoma; however, they lack cytologic features of cancer such as prominent nucleoli.
Post-atrophic Hyperplasia - Higher Magnification
This case is not difficult to distinguish from prostatic adenocarcinoma. In challenging cases, the immunostain for high molecular weight cytokeratin is invaluable
Hyperplasia of the median lobe of the prostate produces a polypoid mass that protrudes in the bladder lumen.
Basal Cell Hyperplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Basal cell hyperplasia is usually seen in the transition zone. Occasionally, it may be encountered in needle biopsies (which sample peripheral zone).
Basal Cell Hyperplasia - Higher Magnification
The nuclei are ovoid or round with finely reticular chromatin and rare punctate nucleoli. The cytoplasm is pale eosinophilic or clear
Clear Cell Cribriform Hyperplasia
Lobular clusters of glands with cribriform architecture
Clear Cell Cribriform Hyperplasia
The glandular clusters have punched out lumens. The cytoplasm is clear or pale eosinophilic. The nuclei are uniform and lack nucleoli. Basal cells can be clearly seen.
Stromal Hyperplasia with Atypia
Large atypical cells with hyperchromatic nuclei containing intranuclear vacuoles are interspersed between benign glands. Prostatic stromal hyperplasia with atypia
| Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia in Needle Biopsy Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia (adenosis) - when seen in a needle biopsy - is one of the most challenging benign mimics of cancer. A partially sampled focus of cancer may be mistaken for AAH |
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia
AAH encountered in a transurethral resection specimen.
Atypical Adenomatous Hyperplasia - 34bE12 Immunostain
The immunostain for high molecular weight cytokeratin 34bE12 demonstrates fragmented basal cell layer in the previous focus of AAH.
Post-atrophic Hyperplasia
Clusters of atrophic prostatic acini with proliferative changes. At low magnification, it may be mistaken for adenocarcinoma; however, they lack cytologic features of cancer such as prominent nucleoli.
Post-atrophic Hyperplasia - Higher Magnification
This case is not difficult to distinguish from prostatic adenocarcinoma. In challenging cases, the immunostain for high molecular weight cytokeratin is invaluable
Prostate Metaplasia (slides)
Urothelial Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
The central portions of the prostatic ducts are normally lined by urothelium. When urothelial lining is seen in more peripheral ducts and glands as in this needle biopsy, the term urothelial metaplasia is used.
Urothelial Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Note the lack of cytologic atypia which is helpful in distinguishing urothelial metaplasia from high-grade PIN.
Mucinous Metaplasia in Prostate
In this transurethral resection, clusters of mucinous glands lined by tall columnar cells are seen admixed with usual prostatic glands. The mucin is positive for mucicarmine, PAS, and alcian blue. The glands are negative for PSA and PAP.
Mucinous Metaplasia in Prostate
The nuclei are small and basally located and lack prominent nucleoli. The differential diagnosis is with Cowper’s glands and adenocarcinoma.
Mucinous Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Mucinous metaplasia in a needle biopsy of the prostate. Note partial involvement in one of the glands on the right.
Squamous Metaplasia : PSA Immunostain
Mucinous glands are negative for PSA immunostain. Same case as previous slide.
Squamous Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Squamous metaplasia in prostate can be seen in response to infarction, inflammation, radiation therapy, or androgen deprivation therapy
Squamous Metaplasia in TUR Specimen
Squamous metaplasia adjacent to an area of infarction in a transurethral resection specimen
The central portions of the prostatic ducts are normally lined by urothelium. When urothelial lining is seen in more peripheral ducts and glands as in this needle biopsy, the term urothelial metaplasia is used.
Urothelial Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Note the lack of cytologic atypia which is helpful in distinguishing urothelial metaplasia from high-grade PIN.
Mucinous Metaplasia in Prostate
In this transurethral resection, clusters of mucinous glands lined by tall columnar cells are seen admixed with usual prostatic glands. The mucin is positive for mucicarmine, PAS, and alcian blue. The glands are negative for PSA and PAP.
Mucinous Metaplasia in Prostate
The nuclei are small and basally located and lack prominent nucleoli. The differential diagnosis is with Cowper’s glands and adenocarcinoma.
Mucinous Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Mucinous metaplasia in a needle biopsy of the prostate. Note partial involvement in one of the glands on the right.
Squamous Metaplasia : PSA Immunostain
Mucinous glands are negative for PSA immunostain. Same case as previous slide.
Squamous Metaplasia in Prostate Needle Biopsy
Squamous metaplasia in prostate can be seen in response to infarction, inflammation, radiation therapy, or androgen deprivation therapy
Squamous Metaplasia in TUR Specimen
Squamous metaplasia adjacent to an area of infarction in a transurethral resection specimen
Prostate : Inflammation(slides)
Prostate : Acute Inflammation
Prostate : Malakoplakia
Prostate : Post-biopsy granuloma
Prostate : Non-specific Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Non-specific Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Post-BCG Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Post-BCG Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Xanthoma
Prostate : Xanthoma (CD68 Immunostain)
Prostate : Malakoplakia
Prostate : Post-biopsy granuloma
Prostate : Non-specific Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Non-specific Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Post-BCG Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Post-BCG Granulomatous Inflammation
Prostate : Xanthoma
Prostate : Xanthoma (CD68 Immunostain)
Prostate and Seminal Vesicles
prostate gland Normal
Neuroendocrine Cells in Atrophic Prostate Glands

Normal glands
Normal glands - 34bE12 Immunostain
Corpora Amylacea in Prostate Biopsies
Corpora Amylacea in Prostate Biopsies
Prostate - Crystalloids in Benign Glands
Ganglia in Prostate Biopsies
Ganglia in Prostate Biopsies
Ganglia in Prostate Biopsies
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies - Immunoreactivity for Synaptophysin
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies
Perineural Indentation by Benign Prostatic Glands
Pigment in Prostatic Epithelium
Pigment in Prostatic Epithelium
Rectal Mucosa in Prostate Biopsy
Skeletal Muscle in Prostate Biopsies
Spermatozoa in Prostate Biopsy
Seminal vesicle
Seminal vesicle - Older Man
Seminal vesicle - Young Man
Neuroendocrine Cells in Atrophic Prostate Glands

Normal glands
Normal glands - 34bE12 Immunostain
Corpora Amylacea in Prostate Biopsies
| |||||
Prostate - Crystalloids in Benign Glands
Ganglia in Prostate Biopsies
Ganglia in Prostate Biopsies
Ganglia in Prostate Biopsies
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies - Immunoreactivity for Synaptophysin
Paraganglion in Prostate Biopsies
Perineural Indentation by Benign Prostatic Glands
Pigment in Prostatic Epithelium
Pigment in Prostatic Epithelium
Rectal Mucosa in Prostate Biopsy
Skeletal Muscle in Prostate Biopsies
Spermatozoa in Prostate Biopsy
Seminal vesicle
Seminal vesicle - Older Man
Seminal vesicle - Young Man
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)